News & Stories
2026

News
HKUST Develops Novel "Molecular Velcro" to Boost Efficiency and Stability of Perovskite Solar Cells
Researchers from the School of Engineering at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed a robust coating layer that significantly enhances the durability of perovskite solar cells. In tests simulating intense midday sunlight at 85°C, these solar cells retained over 95% of their initial efficiency after more than 1,100 hours of continuous operation. This breakthrough demonstrates the real-world application of perovskite cells in outdoor environments, paving the way for durable, high-efficiency, and low-cost solar technology.

News
HKUST Develops World’s First Sub-Zero Celsius Elastocaloric Green Freezer, Reshaping Freezing Industry with its Zero Emissions
Researchers at the School of Engineering of The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed the world’s first Sub-Zero Celsius elastocaloric freezing device, capable of reaching temperatures as low as -12℃. This represents a significant milestone in expanding green solid-state elastocaloric refrigeration technology into the global freezing industry, offering a promising solution to combat climate change and accelerate low-carbon transformation of the global freezing market. The findings have recently been published in the international journal Nature, under the title “Sub-zero Celsius Elastocaloric Cooling via Low-transition-temperature Alloys”.
News
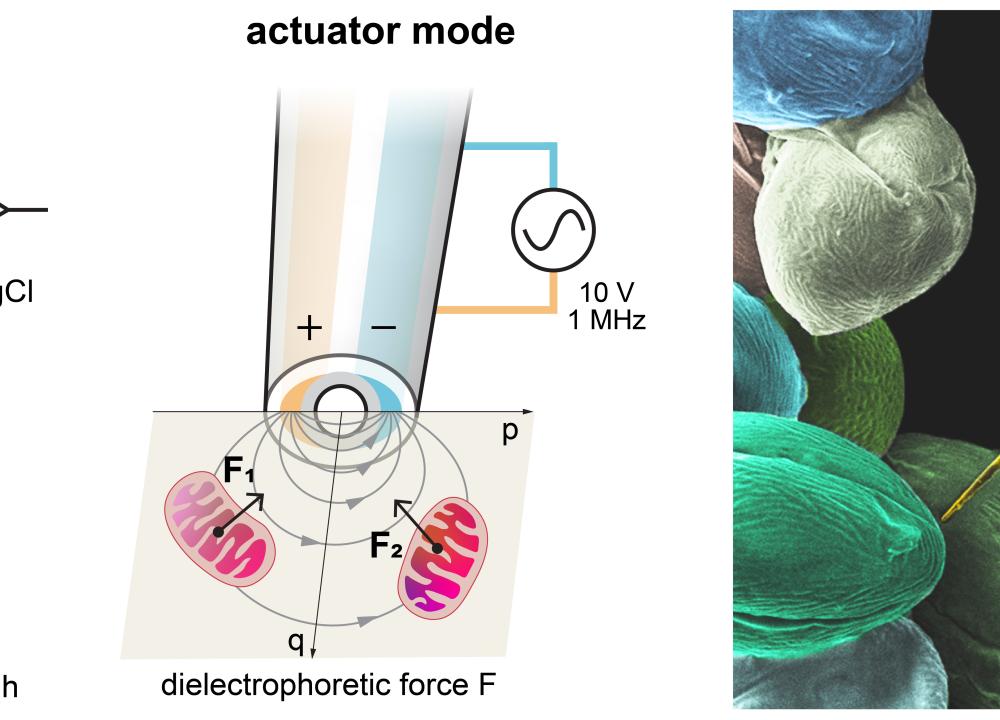
HKUST Co-develops Robotic Nanoprobe for Precise Mitochondria Extraction Charting New Directions in Research on Therapies for Neurodegenerative Diseases and Cancer
Mitochondrial dysfunction is associated with various chronic diseases and cancers, including neurodegenerative diseases and metabolic syndrome. Gently extracting a single mitochondrion from within a living cell—without causing damage and without the guidance of fluorescent makers—has long been a challenge akin to threading a needle in a storm for scientists.

News
13 HKUST Research Projects Secure Top Funding from RGC Collaborative Research Fund and Research Impact Fund
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has demonstrated outstanding research leadership in the 2025/26 Collaborative Research Fund (CRF) and Research Impact Fund (RIF) under the University Grants Committee (UGC)'s Research Grants Council (RGC). The University secured funding for 13 projects under the CRF and RIF, with grants totaling more than HKD77 million. The achievement places HKUST first among all UGC-funded universities in both the number of funded projects and total funding received. This accomplishment highlights HKUST's strength in pioneering interdisciplinary and cross-institutional research, as well as its exceptional capacity for knowledge transfer in translating cutting-edge research outcomes into real-world impact that enhances societal well-being.
2025
News
HKUST Researchers Uncover Key Transport Mechanisms in Cells, Shedding Light on Causes of Genetic Diseases
A research team led by Prof. GUO Yusong, Associate Professor of the Division of Life Science at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has made a significant breakthrough in understanding how cells manage the intricate internal transport of proteins, a process fundamental to life and implicated in several hereditary diseases. By employing an innovative vesicle proteomics platform, the team has systematically identified new cargo proteins and key accessory factors for two critical cellular transport complexes, AP-1 and AP-4. The findings, published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS), combine innovative vesicle reconstitution techniques with quantitative mass spectrometry-based proteomics to unveil a comprehensive map of previously unknown cargo proteins and regulatory factors.
News
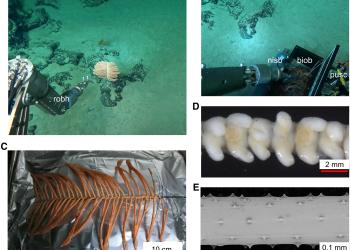
HKUST Researchers Develop Novel Model to Unveil Deep-Sea Black Coral Symbiotic System
A research team led by Prof. QIAN Peiyuan, Chair Professor of the Department of Ocean Science at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), in collaboration with the Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), and the Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute of the Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences (CAFS), has achieved a significant breakthrough in understanding the adaptive strategies of the deep-sea black coral Bathypathes pseudoalternata (B. pseudoalternata) and its symbiotic microbiome. The study has been published in the top international journal Cell Host & Microbe.

News
HKUST Researchers Unlock Why Arctic Ice Melt Paused
A research team led by The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) scholars has discovered a significant slowdown in Arctic sea ice melting since 2012, with the decrease rate of 11.3% per decade to an insignificant downward trend of only −0.4% per decade. This phenomenon is closely related to a shift in the North Atlantic Oscillation (NAO) pattern, from a negative phase to its positive phase, which traps cold air within the Arctic region. It is projected to peak between 2030 and 2040, after which the Arctic could enter a new phase of accelerated ice melt. Without reductions in greenhouse gas emissions, this may trigger severe climate and environmental crises within decades.
News
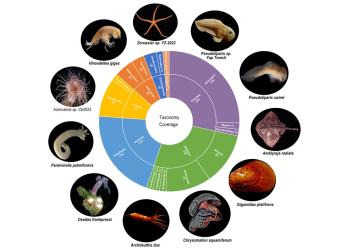
HKUST Launches World's First Deep-Sea Multi-Omics Resource Platform Empowering Global Research into Biological Adaptation in Extreme Environments
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), in collaboration with the Southern Marine Science and Engineering Guangdong Laboratory (Guangzhou), has launched the world's first Deep Ocean Omics (DOO) database (https://DeepOceanOmics.org/). As the largest platform of its kind, DOO integrates and analyzes multi-omics data from organisms thriving in the ocean's most extreme environments, alongside customized analytical tools to support cross-species comparative and evolutionary studies. By facilitating the utilization of deep-sea biological resources, the platform aims to advance scientific understanding of deep-sea biodiversity and ecosystems, and to foster global research and applications related to biological adaptation in extreme environments.








