News & Stories
2026

News
HKUST Achieves First Certified Breakthrough in Fully Solvent‑Free Perovskite Solar Cell Technology
Researchers at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have made a major breakthrough in producing perovskite solar cells. They developed a multi-source co-evaporation recipe that markedly enhances the crystal quality of vacuum-deposited perovskite films. The advance brings all vacuum-deposited single-junction perovskite cells as well as perovskite-on-silicon tandem solar cells closer to scalable production. This breakthrough has been reported in Nature Materials, in a paper entitled “Crystal-facet-directed all-vacuum-deposited perovskite solar cells”.

News
HKUST Develops Novel Calcium-Ion Battery Technology Enhancing Energy Storage Efficiency and Sustainability
Researchers at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have achieved a breakthrough in calcium-ion battery (CIB) technology, which could transform energy storage solutions in everyday life. Utilizing quasi-solid-state electrolytes (QSSEs), these innovative CIBs promise to enhance the efficiency and sustainability of energy storage, impacting a wide range of applications from renewable energy systems to electric vehicles. The findings are published in the international journal Advanced Science titled “High-Performance Quasi-Solid-State Calcium-Ion Batteries from Redox-Active Covalent Organic Framework Electrolytes”.
News
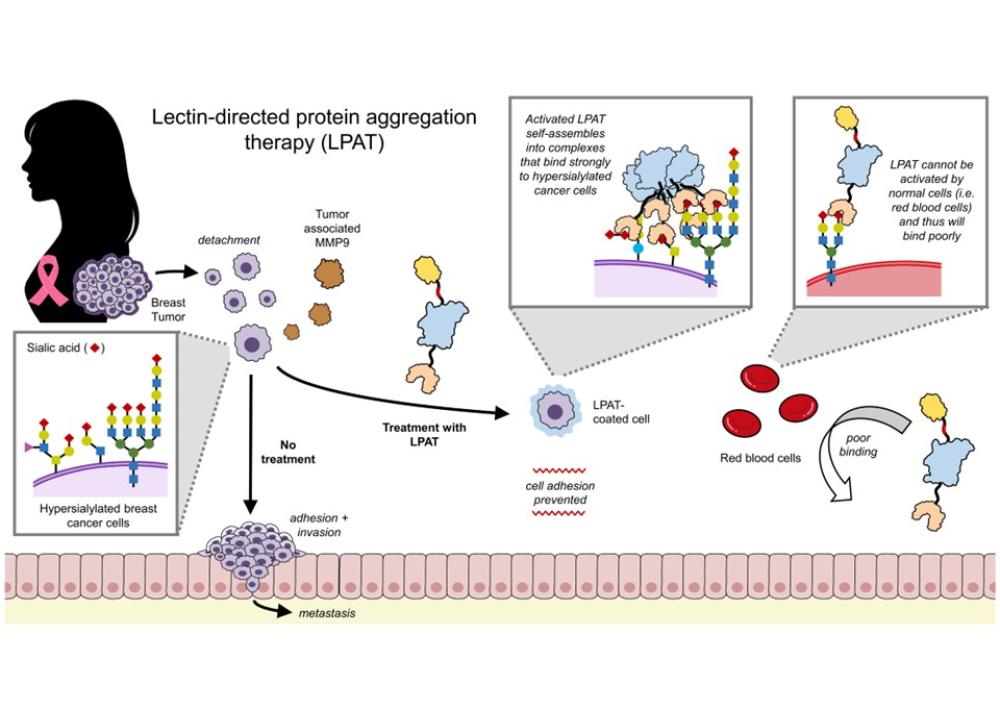
HKUST Researchers Develop Metastasis Prevention Therapy Based on Glycan Targeting
A research team led by Prof. Kenward VONG, Assistant Professor from the Department of Chemistry at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has recently achieved a significant breakthrough by bioengineering a new type of glycan-targeting system known as “lectin-directed protein aggregation therapy (LPAT)”. Using this technology, they developed a therapy capable of preventing the onset and growth of metastatic breast cancers in mouse models.

News
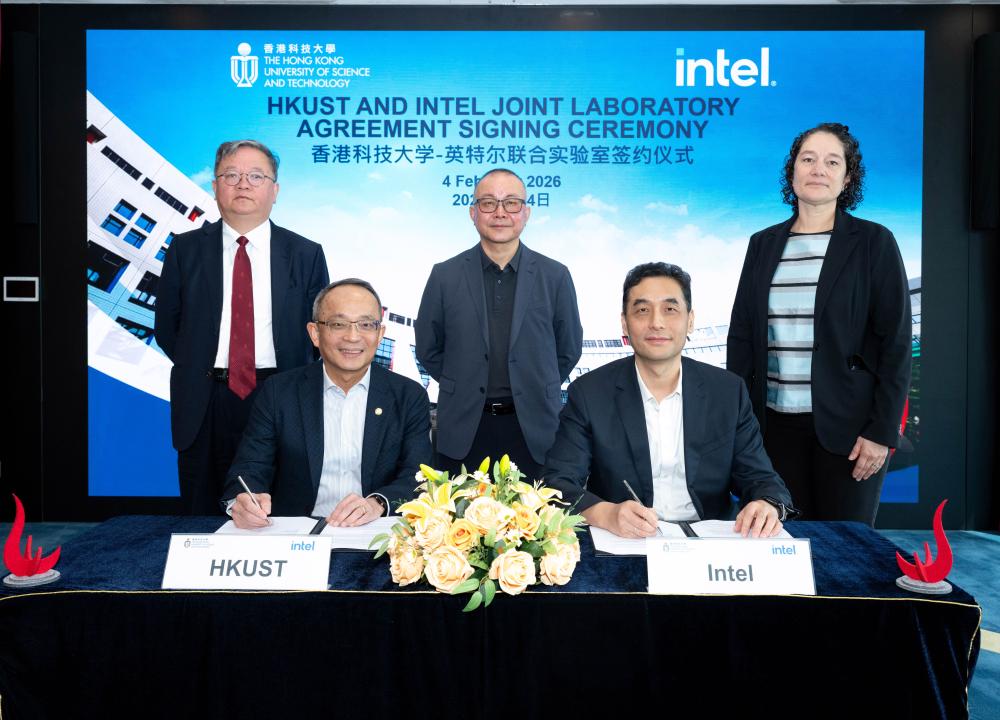
HKUST and Intel Establish Joint Laboratory to Focus on High-Efficiency Intelligent Computing
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) and Intel Corporation (Intel) announced the establishment of the HKUST-Intel Joint Laboratory (Joint Lab). At the heart of the project is a three-year research program that will explore high-efficiency near-memory computing (NMC) architectures for addressing challenges in the performance and energy efficiency of artificial intelligence (AI) applications. Through innovations in software-hardware co-design, the collaboration aims to provide key insights into the future development of intelligent devices and sustainable AI systems.The signatories were Prof. Tim Kwan-Ting CHENG, Vice-President for Research and Development of HKUST, and Mr. SONG Jiqiang, Director of Intel Labs China. Prof. GUO Yike, Provost of HKUST; Mr. WANG Zhicong, Chairman of Intel China, and Ms. Gabriela Cruz THOMPSON, Senior Director of University Research and Collaboration, Intel witnessed the agreement.
News
HKUST Research Reveals Cost-Effective Food Waste Treatment Through Sewage Systems
A research team at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) has developed an innovative urban food waste management framework by analyzing food waste data from 29 large cities worldwide, including Hong Kong, Beijing, and New York. The study shows that in cities with higher food waste moisture loads, such as Hong Kong, grinding food waste and diverting it into the sewage system is more effective than relying solely on landfilling. This approach can reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions by about 47% and lower total waste-management costs by about 11%. The research provides a new, quantitative basis for shaping food waste management strategies in cities around the globe.

News
HKUST Pioneers Computational Models for Transregional Neural Activity to Re-establish Damaged Neural Connectivity, Offering New Hope to Patients
Researchers at The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) School of Engineering have achieved a major breakthrough in computational neural engineering. They have developed a novel reinforcement learning-based generative model to predict neural signals, creating an artificial information pathway that effectively bypasses damaged brain areas. This groundbreaking research opens up new possibilities for neural rehabilitation in patients suffering from motor or cognitive impairments caused by conditions such as stroke or spinal cord injury. Their study, titled “A generative spike prediction model using behavioral reinforcement for re-establishing neural functional connectivity”, has been published in the prestigious journal Nature Computational Science.
News
HKUST Develops Breakthrough High‑Efficiency, Low‑Cost Wastewater Treatment Technology
The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) research team has developed a groundbreaking wastewater treatment technology that integrates a mesh bioreactor with an ultrasound-induced transient cavitation cleaning mechanism. The system can complete mesh cleaning within 3.8 seconds under anaerobic conditions and achieves 10-20 times higher flux than conventional membrane bioreactors (MBRs). The technology operates efficiently with substantially lower energy consumption, produces treated effluent surpassing international and local discharge standards, and reduces the cost of treating each cubic metre of wastewater to 50% of conventional MBRs, offering a sustainable solution for both municipal and industrial wastewater treatment.

News
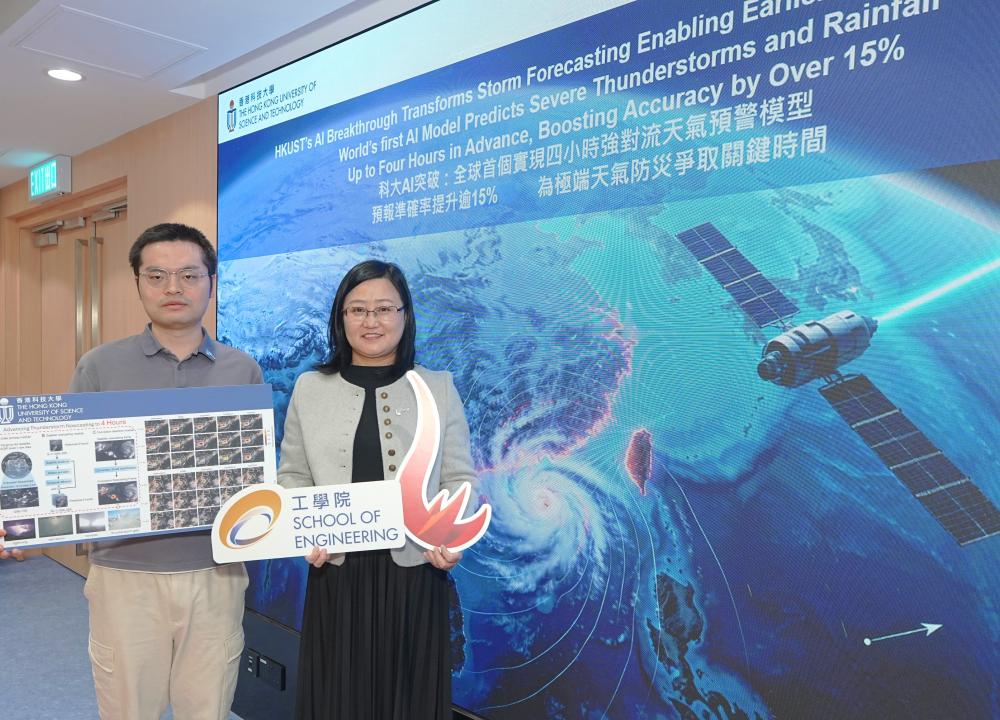
HKUST's AI Breakthrough Transforms Storm Forecasting Enabling Earlier Life-Saving Warnings
In a critical advance for climate resilience, researchers from The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST) have developed an AI model that can predict dangerous convective storms—including Black Rainstorms, thunderstorms and extreme heavy rainfall like those that have hit Hong Kong—up to four hours before they strike. This world-first technology, developed in collaboration with national meteorological institutions and powered by satellite data and advanced deep diffusion technology, improves forecast accuracy by over 15% at the 48‑kilometer spatial scale compared with existing systems. This breakthrough strengthens the overall accuracy of the national weather forecasting system and promises to transform early warning systems for vulnerable communities across Asia.








